Table of Contents
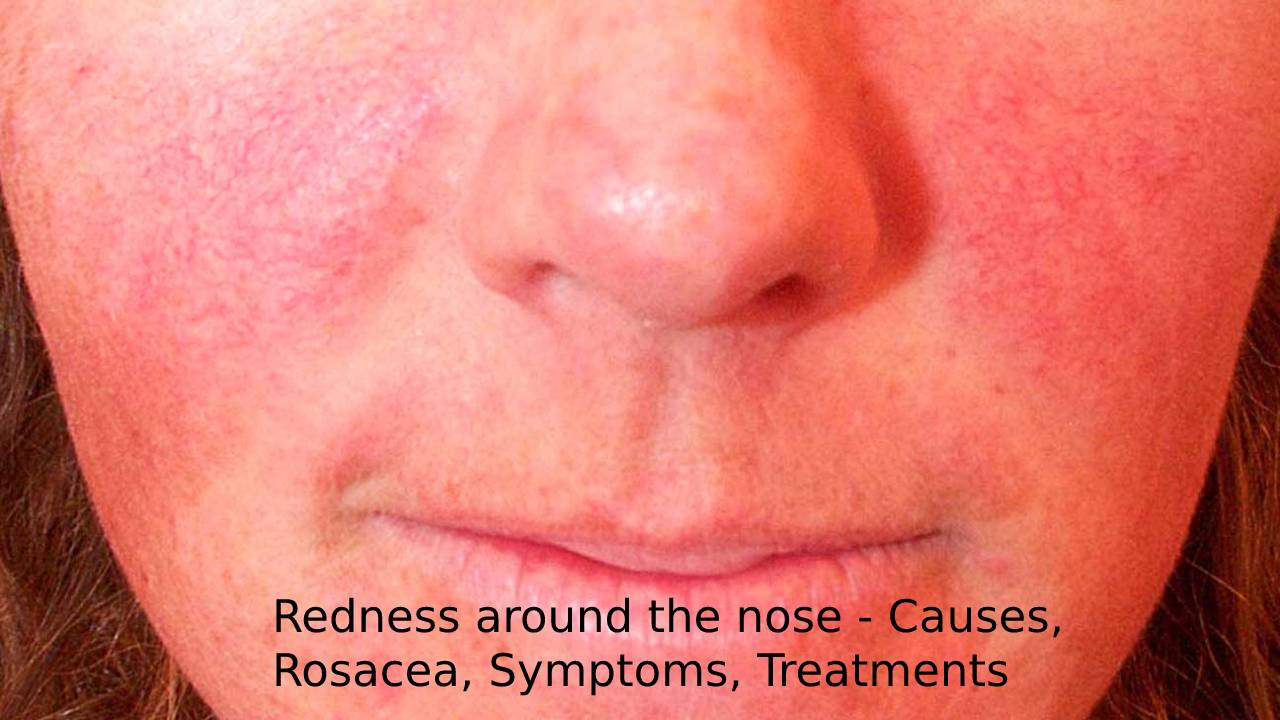
Redness around nose
Redness around the nose is temporary redness, which is not uncommon.
External factors like cold air, wind, and allergens can trigger delicate skin just below the lips and around the nostrils.
You may be looking for answers because you are prone to this symptom and want to know if you should be concerned, or you may just be looking for a quick way to treat it.
This article looks at various possible reasons for nose redness, treatment ideas, and ways to prevent redness.
Most people have a red nose after a cold, flu, or allergic reaction. In these cases, the redness is usually due to dry skin resulting from prolonged cleansing.
The nose can also turn red from skin and blood vessel problems, chronic inflammation, allergies, and a few other medical conditions.
While a red nose can be bothersome, it is rarely a cause for concern.
Causes of Red Nose
- Not only does a red nose look a bit strange, but it can also result from an illness.
- Most people think when they see a red nose, which may also be a bit bulbous and large-pored, excessive alcohol consumption.
- However, the cause is often a skin condition called Rosacea.
- A massive runny nose, sunburn, and cold can, of course, also cause an acutely red nose.
- Beautiful, slightly rosy skin, especially on the face – that is our ideal of beauty.
- However, some people have reddened skin that they find less attractive or even signs of serious illness.

Rosacea
- “Rosacea is a skin disease that repeatedly manifests itself in the form of redness and inflammatory changes in the skin.
- Those who avoid triggering triggers and use a calming and protective skincare line can visibly stabilize the skin condition. “
- Rosacea, also known as “copper rose,” shows itself on the face, initially through reddening of the skin, which mainly affects the middle third of the face.
- These are cheeks and nose; this redness occurs suddenly and only stays there for hours – or days. The blood vessels are dilated.
- Rosacea is an inflammatory virus that occurs in bursts. The redness of the skin itchy or burn and develop into papules and pustules over time.
How does Rosacea occur?
- The causes of Rosacea are not exact. An immune reaction against the hair follicle mite (Demodex folliculorum), which colonizes the skin in many people, but to a greater extent in those with Rosacea, is an option.
- The temperature regulation in the brain could also be disturbed. Papules and pustules are visible signs of inflammation.
- The immune cells that migrate into the affected skin areas release messenger substances that cause them to widen.
- As a result of the inflammation, the connective tissue and sebum glands’ cells divide excessively – the skin is thickened in places and appears to have large pores.
- Genetic factors play a part in the development of Rosacea. Many of those affected have family members who are also sick.
- Different triggers, called “triggers,” can cause new attacks in those affected. These include spicy foods, hot drinks, alcohol, stress, cosmetics, or medication.
- Cold and wind are not suitable for the skin; heat and sunlight are particularly harmful.
Types of Rosacea
1. Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea
- It causes noticeable redness, flushing, and blood vessels.
2. Rosacea of the eye
- It irritates the eyes and eyelids but does not usually affect the nose. However, people with this form of Rosacea can develop other types of Rosacea.
3. Ocular Rosacea
- It thickens the skin and develops an uneven texture.
4. Papulopustular Rosacea
- It causes acne, redness, and swelling.
Stages, Symptoms, Treatment of Rosacea
- The reddening of the face occurs intermittently and with different symptoms depending on the severity.
- The first sign in the early stages is a superficial reddening of the face, especially around the cheeks, nose, and forehead.
- This redness is caused by an increased blood flow and an excessive expansion of small veins in the affected area.
- In later stages, the skin becomes more sensitive due to inflammation and burning, and itching. Rosacea generally occurs in phases over several years.
Pre-stage- Rosacea diathesis
- Volatile and sudden reddening of the skin (erythema), also known as flushing, is typical for this first phase of Rosacea.
- This redness usually goes as fast as it came and mainly affected the cheek, nose, chin, and middle forehead area.
- The reddening rarely extends to the neck, chest, or nape of the neck. Light Rosacea benefits from skin-soothing care:
- The Antirougeurs line from Avène, for example, relieves redness, has a decongestant and vasoconstricting effect.
Symptoms of Rosacea
- Reddening of the skin on the face
- Sensitive skin
- Itching, burning, stinging of the skin
- Inflammatory vesicles
- Aching nodules
- Lymphedema
- Bulbous growths (bulbous nose)
How to treat redness of the nose?
- Rosacea is treatable, but some people with Rosacea develop permanent redness on the skin.
- Rosacea Redness is treated differently than redness affected by other conditions.
- Avoid ingredients witch hazel and menthol, which are found in many toners and other exfoliating products.
- Prescription topical ointments can be used for the redness treatment. Laser treatment is also an excellent treatment option for persistent rosacea redness on the face.
Lifestyle recommendations
- People with Rosacea generally need to find out what triggers their symptoms to reduce their relapses’ frequency.
- Common triggers are spicy food, alcoholic beverages, and prolonged exposure to the sun.
- People with Rosacea should also use sunscreens or physical blockers with a high SPF such as zinc oxide, as well as sun-protective clothing.